Newton's First Law Of Motion
Newton's First Law Of Motion
In our everyday life we observe that effort is required to put a stationary object into
motion or to stop a moving object. Have you ever wondered if a ball, kicked on the ground,
would keep moving forever, or, after some time would it naturally stop moving? Until
Newton, most people thought the ball would eventually stop on its own.
However, the ball will continue to move unless an object or force stops it. Here comes Newton's
First Law which states: A body continues to be in its state of rest,
or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
This means that there is a natural tendency of objects to keep on doing what they're doing.
All objects resist changes in their states of motion. In the absence of an unbalanced
force, an object in motion will maintain this state of motion.
To understand Newton's First Law, you need to understand what unbalanced force is.
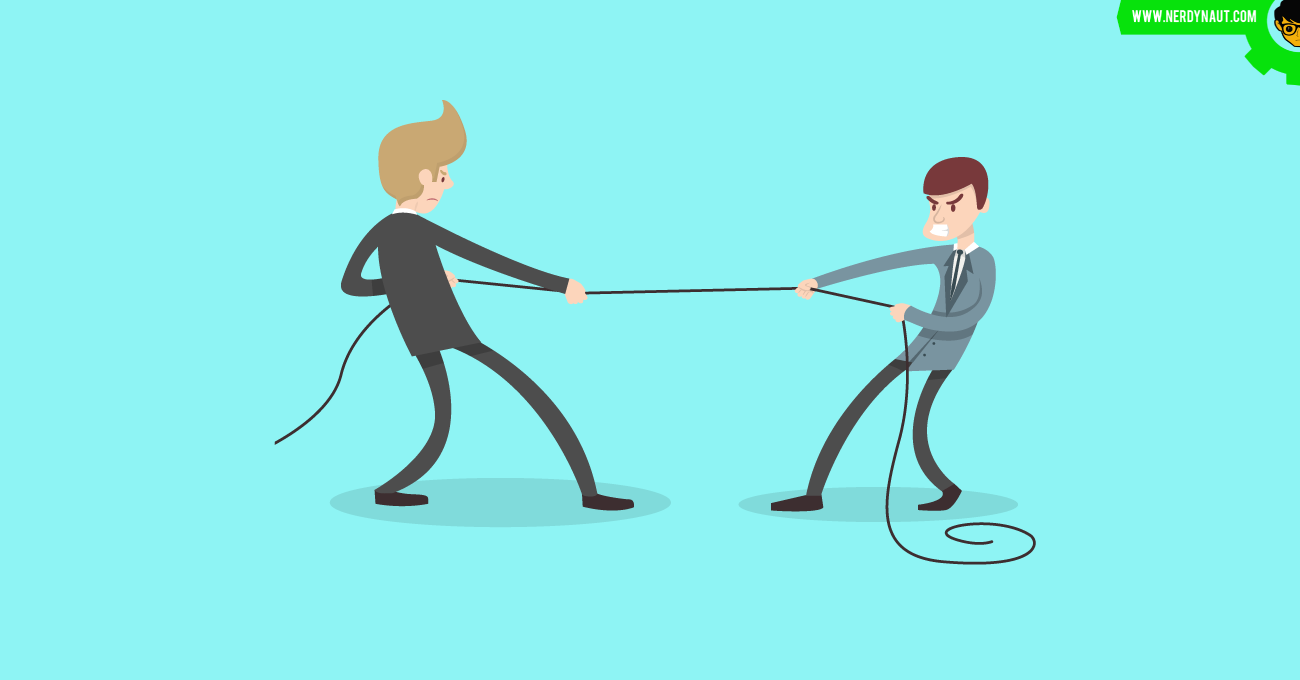
If you have seen a game of tug of war, you would have seen two teams pulling a rope in
opposite directions. If the rope doesn't move, the forces applied by the teams are balanced
forces, as they are of equal magnitudes in opposite directions.
If one of the teams applies a greater force, it pulls the other team and the rope towards
their side. In this case, the forces are unbalanced as the two forces are of unequal magnitudes
in the opposite directions. If one of the team lets go of the rope, the opposite team
falls backwards. This tendency to fall backwards, despite letting go of the rope is due to inertia.
That is, if an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest and if it is in motion,
it tends to stay in motion. This property of an object is called its inertia. Inertia
is the resistance an object has to a change in its state of motion.
Inertia can be classified into three categories: Inertia of rest
Inertia of direction Inertia of motion
Certain experiences that we have while travelling in a bus can be explained on the basis of
the Law of Inertia.
When a passenger is standing in a stationary bus that suddenly moves, the movement pushes
the passenger backward. Why does this happen?
This is due to the Inertia of Rest experienced by the passenger in the upper part of his
body. The body is at rest when the bus is at rest.
When the bus starts all of a sudden, the lower part of body is in contact with the vehicle
that started moving, whereas the upper part of the body continues to be at rest because
of the Inertia of Rest. Inertia of rest is the tendency of a body
to resist any change in its state of rest. What happens when a fast moving bus negotiates
a right hand curve on the road? The passengers will tilt to the right.
This is due to the inertia of direction.
Inertia of direction is the tendency of a body to oppose any change in the direction
of its motion. With the application of sharp brakes, the
bus stops all of a sudden and the passengers tend to fall forward. This is due to inertia
of motion experienced by the upper part of the body.
When the bus is moving, the whole body of the passenger is in a state of motion. A sudden
halt caused the lower part of the passenger's body, that is in contact with the bus, to
come to rest. However, the upper portion of his body remains in the state of motion, due
to the inertia of motion, causing the passenger to fall forward when the bus stops suddenly.
Inertia of motion is the tendency of a body to resist a change in its state of uniform
motion. Thus, Newton's First Law is also called, 'The
Law of Inertia'. Well, now this law should make sense.
Now do you understand why a ball on the ground, after being kicked does not keep moving forever?
The ball stops after some time due to the unbalanced external force applied by the ground
in the opposite direction.
THINGS TO REMEMBER
Newton's First Law of Motion states that 'A body continues to be in its state of rest
or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force'.
Two unequal oppositely exerted forces are called unbalanced forces.
Newton's First Law is also known as the Law of Inertia.
The tendency of an object to continue its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight
line is called inertia. The three types of inertia are: inertia of
rest, inertia of motion and inertia of direction.

No comments:
Post a Comment